Overview
Endoscopic Examination
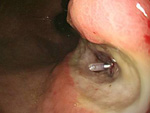
The endoscopic examination is a test where an endoscope is inserted through the mouth or anus to examine and treat organs such as the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and colon, as well as the bile duct and pancreatic duct. Japan is the global leader in the Endoscopic examination field.
Our hospital uses the latest examination/treatment equipment and techniques to detect diseases at an early stage through physical examinations, medical checkups and screenings. We also conduct thorough examinations on patients introduced to us from other facilities, and endoscopic treatments for early stage cancer (esophagus, stomach, colon, etc.).
We also provide care for benign diseases and emergency diseases such as acute cholangitis due to gallstones, and hematemesis/melena from gastrointestinal hemorrhage(gastroduodenal ulcer or esophageal and gastric varices.)
There are many patients who worry that fiberscopes and endoscopic examinations are uncomfortable. At our endoscopic room, doctors, nurses and endoscope specialists work together and strive to conduct a pain-free, safe and accurate endoscopic examination/treatment. Please feel free to contact us about endoscopic examinations.
Endoscopic Treatment Details
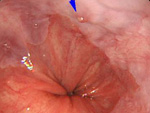
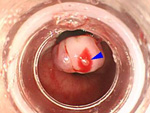
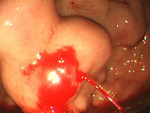
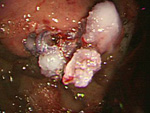
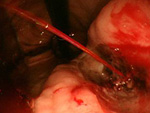
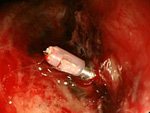
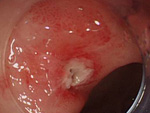
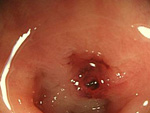
1. ESD、EMR
- 1)Esophageal ESD
- 2)Gastric ESD
- 3)Large Intestine
- ESD
- EMR(polypectomy)
On Endoscopic treatment (EMR, ESD) for Digestive Cancer (esophagus, stomach, large intestine)
- Introduction
The Stage IV digestive cancer does not have a good prognosis and early detection and treatment by an endoscope is essential to defeat it. The development of endoscopes in recent years has made early-detection of digestive cancer possible
Treatments such as the Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) and the Endoscopic Sub-mucosal Dissection (ESD) are digestive cancer treatment methods that are minimally invasive and preserve the quality of life (QOL). Many cancer patients have previous medical history so in order to provide the best endoscopic treatment, it is important to set up a stable whole-body and preoperative care.
- EMR
EMR is an endoscopic treatment for relatively small, early-stage cancers.
- ESD
ESD is an endoscopic treatment conducted for major lesions and scar lesions that could not be removed with the EMR. ESD is especially important for esophagus cancer treatment where the invasiveness between a surgical operation and endoscopic treatment differ the most.
- Treatment Results at our Department
- A specialist thoroughly familiar with emergency endoscopy for gastrointestinal hemorrhage and acute cholangitis will conduct the operation. For post-operation pathological examinations and radical excisions, an en bloc resection is ideal. Our hospital actively conducts ESD not only for the stomach but for more challenging areas such as the esophagus and colon. As a general hospital, most of our patients are elders with various previously diagnosed diseases. By working closely together with other departments, we are able to conduct a stable, whole-body preoperative care for the heart, lung, kidney and various organs. Some other characteristics of our hospital’s ESD treatment is the combined use of flex knife and ST hood which is an excellent strategy, yielding good treatment results and low complication rates.
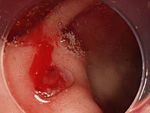
2. Gastroduodenal Ulcer Consultations
“Gastroduodenal Ulcer” is a disease in which stress, smoking, drinking, painkillers or heart disease medication causes damage on the stomach or duodenal mucosa.
If left untreated, it causes bleeding and leads to hematemesis or melena. Our department conducts emergency endoscopic examinations 24 hours a day.
After hemostasis treatment, ulcer treatments continue through hospitalization/outpatient consultation. Examinations are conducted to make sure that the stomach cancer does not complicate, and treatments are available for Helicobacter Pylori, which is the biggest cause for ulcers.
3. ERCP (Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)
ERCP is an examination and treatment method using an endoscope for diseases related to the pancreas and biliary tree (jaundice and pancreatitis from choledocholithiasis, malignant tumors such as pancreatic cancer and bile duct cancer).
This examination is conducted for symptoms such as abdominal pain and jaundice, or when there are abnormalities in blood test results or image diagnosis (abdominal CT, abdominal ultrasound and MRI examinations).
The condition when the disruption of the bile duct flow caused by gallstones and malignant tumors sets off clinical conditions such as jaundice and infections, is called obstructive cholangitis. When jaundice, abdominal pain and inflammation worsens, an emergency examination must be conducted as it may be deadly.
Our department has doctors, specialists and nurses ready 24 hours a day.
The biggest complication for ERCP examinations is pancreatitis, but our hospital conducts a relatively safe examination with a rate of 0.4% (nationwide research shows an average of 2-5%).
We offer stent (metal tube) treatment for patients to live comfortably, even under pancreatic cancer and bile duct cancer (treatments which are considered difficult to this day), compression of the bile duct from other malignant tumors or chemotherapy to improve jaundice.
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
To provide consultations centered on endoscopic treatment, we cooperate with other departments to form a system that can conduct emergency endoscopic examinations 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, for gastrointestinal bleeding that occurs within and outside of our hospital.
Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage and Endoscopic Therapy
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Treatment
IBD is a chronic illness with unknown causes. However, if a patient stays in remission, they are able to work, get married and give birth with little chance of the disease affecting their life. However, a patient coping life with IBD symptoms is not our goal. The initial treatment is important in order to control inflammation and rid all symptoms. The next step is to find out a safe treatment method that can sustain remission. We aim to improve the patient’s QOL by having them examined, and after considering advantages and disadvantages, provide the earliest possible remission induction and long-term remission permanence.
If it is a mild to moderate case of UC, we conduct treatment based on oral/enema 5-ASA drugs (Pentasa, Asacol, Salazopyrin), and suppositories. 5-ASA drugs are not only basic medication for UC that reduces inflammation, but also effective for maintaining remission. The use of steroid drugs should be avoided as much as possible. If 5-ASA is not effective or if the patient has allergies to it, Azathioprine (Imuran) will be administrated.
For patients with prolonging inflammation or active lifestyles, we advise blood cell component absorption removal method from an early stage, without using steroids. If this treatment method is chosen carefully, considering severity and adaptability, it is a safe and effective treatment method with minimal side-effects. However, steroids may be used simultaneously if there is severe inflammation, since the blood cell component absorption removal method’s effect may not be sufficient. With simultaneous treatment, an even better outcome and decrease of steroid usage is anticipated. Our hospital has a dialysis center with specialists who will provide treatment.
If the patient presents severe symptoms, we will consider continuous cyclosporine infusion therapy along with consideration of surgery, without conducting steroid therapy. Reiterated use of steroids and cyclosporine without any effectiveness will worsen body conditions and risk overlooking the right timing for surgery. In order to avoid this situation, the careful selection of initial treatment and close examinations of the effectiveness of treatment and body conditions on a short-term basis is necessary.
Recently, the use of anti-TNF-α Infliximab antibody (Remicade) and Tacrolimus (Prograf) has been admitted, and it proactively used when steroid treatment and blood cell component absorption removal method are not effective.
5-ASA drugs (Pentasa, Salazopyrin) and nutritional therapy (Elental) are used to control Crohn's Disease, but when they are not sufficient, we will conduct an anti-TNF-α Infliximab antibody (Remicade) or Adalimumab (Humira) treatment without any usage of steroids. Out hospital has an outpatient IV Center where our specialists familiar with this treatment offer therapy. If these treatments are not enough, or if 5-ASA drugs cannot be used due to side-effects, we may use the Oral Immunosuppressive AZA (Imuran).